In the early days of digital identity and SSI, Trust Registries were a great starting point to prove who we are online. They acted like verified lists, showing which organisations or issuers could be trusted to issue credentials. Simple and effective for where the ecosystem was back then.
But the world has changed. We’re now entering an era of AI agents, decentralised systems, and constantly shifting digital relationships. In this environment, static lists just don’t cut it anymore. Trust isn’t something you tick off once, it’s something that needs to grow, adapt, and be reverified as people, organisations, and agents interact.
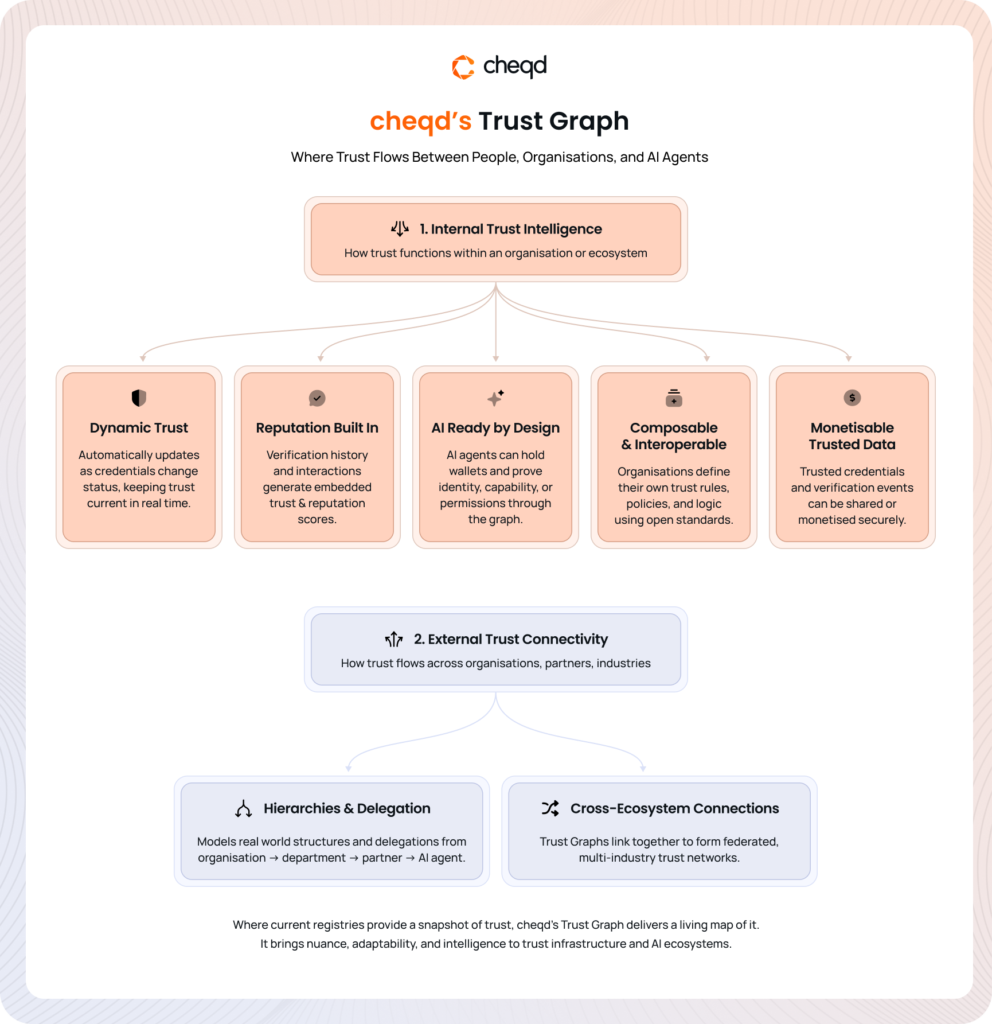
That’s why cheqd is moving from Trust Registries to Trust Graphs. Instead of a simple list, a Trust Graph maps the rich, living connections between people, organisations, and AI agents, showing not just who is trusted, but how, why, and to what degree. It’s a more dynamic and connected way to represent trust in the digital age.
The Limitations of Traditional Registries
Most of the trust systems on the market today are built around the idea of registries: structured lists that record which entities or issuers can be trusted. Registries are static by nature. Once someone or something is added, they stay there until a human updates the entry. There’s no automatic way to show how trust changes, how strong that trust is, or how it connects to others. They’re also isolated, each registry typically sits in its own silo, without the ability to connect to others or share context across ecosystems.
This creates a binary trust model, meaning you’re either trusted or you’re not. There’s no room for reputation or situational context. That’s a serious limitation, especially for AI ecosystems that rely on continuous verification and fluid collaboration.
Trust Graph — Goes Beyond the Market’s
cheqd’s Trust Graph takes things to a completely different level.
A Trust Graph is a living, interconnected network that shows how trust flows between people, organisations, and AI agents. It maps the relationships, hierarchies, permissions, and reputation signals between them. Think of it as a constantly evolving web of trust rather than a static spreadsheet.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
- Dynamic by design: Trust Graphs adapt automatically as credentials are issued, verified, or revoked. This means trust is always up to date, without relying on manual updates or static approvals.
- Hierarchical and contextual: They reflect real-world structures, like organisation → team → AI agent, showing who delegates authority to whom. Trust can cascade or be limited based on context, whether for compliance or access control.
- Cross-connected: Multiple Trust Graphs can link up, which indicates that one company’s graph can connect with another’s, forming a broader network of verified relationships.
- This creates federated or decentralised trust across industries and ecosystems.
- Trust and reputation scores: Because the graph keeps track of verification history and interactions, it can generate trust scores and reputation indicators. These can even be embedded directly into digital identifiers, helping systems instantly assess credibility.
- Fluid and scalable: In AI environments where agents are constantly being created, updated, or retired, the graph structure naturally scales. It’s flexible enough to grow as ecosystems expand, without losing accuracy or control.
Where current registries provide a snapshot of trust, cheqd’s Trust Graph delivers a living map of it. It brings nuance, adaptability, and intelligence to trust infrastructure and AI ecosystems.
The Competitive Edge of cheqd’s Trust Graph
What makes cheqd’s Trust Graph shine is how it ties everything together. It combines the best parts of decentralised identity, verifiable credentials, and trust infrastructure into one flexible, future-ready framework.
On the infrastructural level, the Trust Graph integrates Verifiable Credentials, Trust Registries, and DID-linked Resources into a single network. Every relationship, permission, and credential is anchored by cryptographic proofs, ensuring integrity and verifiability across systems. And because it’s built on open standards like W3C and Trust over IP, it’s interoperable by design, meaning it can plug seamlessly into other ecosystems rather than locking you into one.
Here’s what gives cheqd’s Trust Graph a real edge:
- AI-Ready
It’s built for the world of AI Agents where digital entities act, transact, and make decisions on behalf of humans or organisations. Each agent can hold its own wallet, receive credentials, and prove identity or capabilities securely through the graph. It’s the trust layer for the agentic web. - Hierarchical and Cross-Linked
Trust Graphs represent complex, real-world relationships, like an organisation delegating authority to departments, partners, or AI agents. And since graphs can link across ecosystems, they support federated trust networks that scale globally. - Composable Trust
Every organisation can define its own trust rules, frameworks, and policies, then connect them with others. This creates a flexible, composable system of trust that mirrors how collaboration works in real life — decentralised but connected. - Reputation Embedded in Identity
Trust and reputation are no longer abstract concepts. With cheqd, these attributes can be embedded directly into digital identifiers, powered by verifiable credentials and comes with interaction history. This lets systems instantly gauge credibility without relying on static approvals. - Trust You Can Monetise
Trusted data itself becomes an asset. Credentials and verification events can be packaged, shared, and monetised securely, opening up new streams to create business value. - Future-Proof and Interoperable
While digital identity, AI, and reputation systems develop, cheqd’s Trust Graph is built to adapt and scale alongside them. Based on open standards, it’s fully interoperable and ready to evolve with whatever comes next.
cheqd’s Trust Graph doesn’t just record who’s trusted. It enables ecosystems to build, prove, and monetise trust at scale. It’s the missing infrastructure that makes the next generation of AI and identity truly verifiable.
Redefining How Trust Works
cheqd’s decision to shift from Trust Registries to Trust Graphs marks a major change from static lists of verified entities to living, breathing networks of trust that adapt in real time.
With our offerings, organisations can move beyond simple verification to build trust networks that grow smarter with every interaction, linking humans, agents, and organisations through verifiable, monetisable trust data.
Get in touch at [email protected] to learn more about how to build your own Trust Graph with cheqd.



